Before going straight to the dumbbells, let us first understand the scientific basis of isokinetic exercise. Scientists and researchers from opposite poles of the earth have something to say. Physicians from all over the world are struggling to define a unique pattern of isokinetic workouts. As any two bodies of the universe are not similar, so the body goals are also diverse. Consequently, this particular strength workout regime cannot be confined to any one variety.
Various forms of isokinetic exercises are formulated to help the health-conscious population to make their dream body a reality. Along with the procedure and development of the isokinetic regime, we will also try to differentiate between isokinetic and isotonic forms of workout. Let’s stir up the isokinetic exercise for your peeps.
WHAT SCIENCE SAYS ABOUT ISOKINETIC EXERCISE?
Moldover and Borg-Stein in their second edition of Physiological basis of Rehabilitation Medicine described isokinetic exercises to be a class of workout routine that involves some special accommodation. The special accommodation in isokinetic training refers to the dynamometer. The major role of this special kind of machinery or dynamometer is that it provides a constant velocity during the stage of muscle contraction. High-School science check: velocity can be measured by determining the ratio of displacement to time.
Dynamometer helps in controlling the amount of strength the users are exerting on it. The most common example one can imagine while reading about dynamometers is a stationary cycle. Think about it. Unlike an automated treadmill, a stationary cycle cannot determine the strength you exert during the workout session.
In Moldover and Borg-Stein’s research, the dynamometer used was able to generate graphic documentation of a subject’s output. The machine employed during the isokinetic exercise allows the individual to exert their maximum strength consistently. The dynamometer also applies a corresponding force for maintaining the velocity of contraction. This is a basic scientific explanation of isokinetic exercise spared by Moldover and Borg-Stein in 1994. Several modifications on the rudimentary design of the dynamometer had taken place through the essence remained the same.
WHAT IS ISOKINETIC EXERCISE?
Isokinetic exercise, to be defined simply, is a type of strength training. The isokinetic exercise allows cent per cent muscle contraction during a whole cycle of joint movement. All forms of isokinetic exercises engage a special kind of equipment. The equipment allows the users to exert as much strength as possible. In turn, it provides a series of fluctuating resistance to maintain the pace of the exercise. Another characteristic property of this kind of exercise is that it helps to carry on a constant speed.
The users of the equipment while performing the isokinetic exercise are free to adjust their exercise speed as well as the range of motion. Different attachments and cables in the dynamometer help fix distinguished targets for specified muscle groups. To plan for our immediate routine with isokinetic machines, let us first understand the technicalities involved.
EXAMPLES OF ISOKINETIC EXERCISE
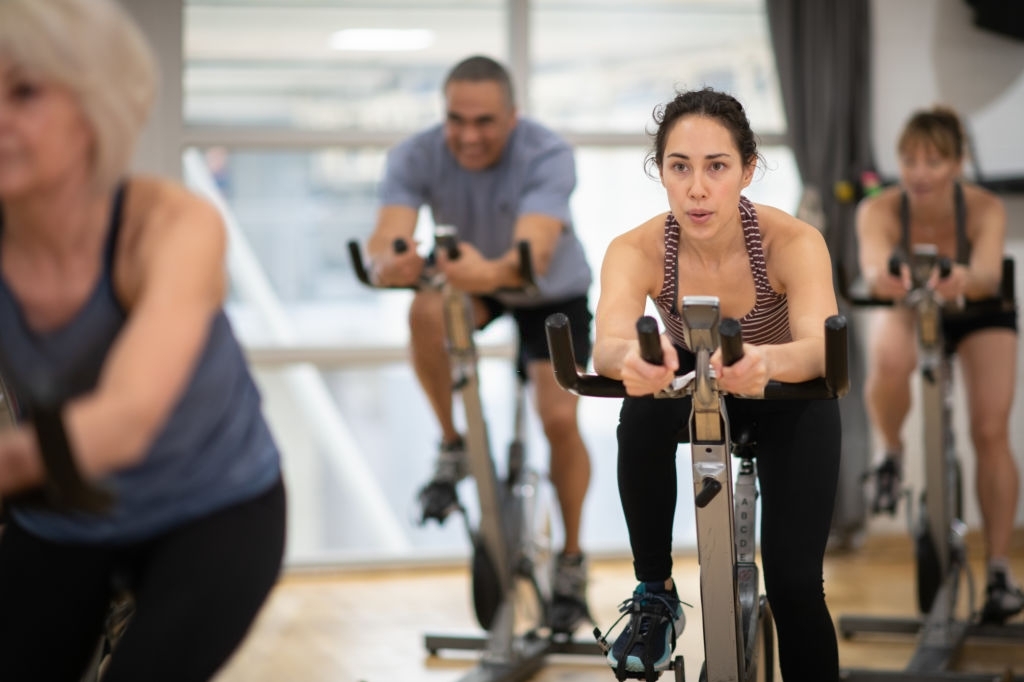
The most common form of isokinetic exercise is a stationary bike or cycle. The stationary bike responds to the constant leg movement of the user. As the pace of the user escalates, the bike is providing resistance to the strength exerted. Though the resistance provided by the bank may vary. The rpm (or rotations per minute) stays the same.
Another controversial example of an isokinetic exercise is the treadmill. According to some experts, the treadmill is unable to provide an equal and opposite resistance and thus, strength workouts are hampered. While, in others’ opinion, the resistance is supposed to vary in the isokinetic regime. No matter what they say, treadmill or no treadmill, walking, and jogging would at least strengthen your cardiovascular functioning.
A BRIEF EXPOSURE TO ISOKINETIC MACHINE
The history of the revolutionary tool tells a different story. It was primarily designed to meet medical needs. The isokinetic exercise equipment was designed to help people restore the strength of their muscles after an injury or accident. Musculoskeletal rehabilitation was the focus of the isokinetic exercise machine, also known as a dynamometer. The machine was used for rehabilitative purposes when it was first constructed in the 1950s.
The researcher intended to measure, evaluate, and influence the strength of muscles along with the range of motion of one’s joints. By the late 1970s, isokinetic machines were found in almost all countries. The use was not anymore limited to medical and rehabilitative needs. Isokinetic machines now became permanent members of the fitness industry. A quick timeline of the development of the latest variety of isokinetic machines is as follows:
- The first isometric measurement system was named Hettinger Dynamometer which was developed in the 1950s
- In 1967, the isokinetic machine was constructed in the United State of America and was named CYBEX 1. This variation of the isokinetic machine was speed controlled and provides a constant speed of propagation.
- Another variation of an isokinetic machine called CYCOB is introduced in Europe in the year 1976.
Now, you may ask what are the major components of an isokinetic machine that makes it so rewarding in the medical and fitness world alike? Three primary components are found in each variation of an isokinetic dynamometer:
- The first and most crucial component is a computer system which serves as a clinical data recorder
- The central portion called the dynamometer upon which the users exert their strength
- The attachments or cables that are connected to the user’s different parts assess the functioning and strength of specific groups of muscles. The attachments from the monitor may extend to a person’s knees, ankles, elbows, shoulders, wrists, etc.
The isokinetic machine, in turn, can be broadly categorized into two sub-types. The type-I isokinetic machine also referred to as an active dynamometer and the type-II isokinetic workout equipment. In the prior one, the speed of the machine remains constant while the resistance to the force exerted on the attachments is variable. Type-II specializes in coinciding the moment arm of the selected resistance and the simultaneous muscle effort. Discover more about isokinetic exercise machines from this article.
From the above discussion, it is clear that isokinetic machines or dynamometer is the central component behind the whole workout regime. After getting a crystal idea about how the machine works, we are ready to dig deeper into the isokinetic regime.
WHAT HAPPENS DURING AN ISOKINETIC WORKOUT?
The climacteric property of isokinetic exercise is workout out amongst the different levels of resistance. The engagement of the machine with the workout regime helps in the creation of resistance. The resistance is crucial to match the strength applied by the user to maintain a constant pace. Apart from the fitness fanatics, isokinetic exercises are highly recommended for individuals trying to recover their muscular strength after an unprecedented event.
Also, the isokinetic regime is beneficial for treating obesity and osteoarthritis as well. Get a medical insight about the exercise from here.
Different machines are devised to meet the unique needs of body transformation. For instance, the quadriceps, the knee extension goals, and the workout of the abdominal muscles can be achieved from a single type of machine. Though all the varieties are capable of providing resistance. A fundamental process is followed for carrying out the isokinetic exercise:
- The initial stage: One should always kick start their isokinetic exercise regime with minimal or zero resistance. With time, the repetition of the exercise must be increased, and simultaneously the resistance will also build up.
- Using the isokinetic machine: Most of the isokinetic equipment is complex. You will be needing assistance if you are not accustomed to using it. The person helping you out with the machine must know how to document your tests and scores. They should monitor your muscle strength.
Nevertheless, once you get to know the techniques, you are good to go on your own. These are frequently used in sports laboratories and various studies of muscle strength throughout the world. - The reps and sets: If you are using the simplest form of isokinetic machines, such as a stationary bike or treadmill, you can easily go for 30 to 60 minutes each session. If you are working out for at least 3 days a week, your pace keeps accelerating at regular intervals. You will be getting to the pro level in no time at all!
- The strength exercises: When you are going for the isokinetic rounds, do not miss out on the other strength-based exercises you were doing regularly. It is recommended by various physicians and fitness trainers to prep your body for isokinetic by doing other strengths. Go for your regular 2 to 3 sets. 8 to 15 reps in each set will be more than just enough.
- Use of weights: Alert! isokinetic exercises ask you to fatigue your muscles while strength is exerted. Please do not overdo your weights. They can strain your muscles. Now we don’t want to count our medical bills, do we?
Sounds easy enough, right? Then what are you waiting for! Go and fix an appointment with your trainer as soon as possible. Schedule your isokinetic workout regime. Flex those muscles. Oh, but yes. Keep the following safety tips handy:
- Do not jump for strength training without prepping your body. Warm-up exercises are much more important than completing your fitness goals before the date. Surprise! Warmups help in enhancing your cardiovascular health.
- You can include stretches, one spot jogging, brisk walking as your prep-up routine for the isokinetic.
- Hydration is the next important task. Keep your body hydrated. Take a lot of water and maintain the ionic balance of your body. Strength-based routines are strenuous. Your body will need every last drop of the minerals.
- STOP the routine in between if you feel uncomfortable. Breath. Cool off. Then start again. It would not affect your regime.
- To avoid overloading, take regular breaks between each round. Holding a regular pace of breathing is important.
- Go for gentle rounds of stretches after completing the regime. This would help in avoiding body soreness and any kind of injury.
- You would need day-offs during the initial stage of starting the isokinetic exercise routine. Do not force your body if you are feeling pain or discomfort.
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN ISOKINETIC AND ISOTONIC EXERCISES
Isokinetic workouts simply refer to the movements at a constant speed regardless of the strength applied. A constant contraction and extension of muscles are observed in the isokinetic regime. The major takeaway from this kind of exercise is extended muscle strength throughout the workout plan.
On the other hand, isotonic exercises help in shortening the muscles at a constant rate throughout the course of the isotonic workout plan. Isotonic type of muscle contractions is also named dynamic contraction. Most of the exercises that we witness in our daily lives are isotonic in nature. The workouts carried out with the help of dumbbells and barbells help in shortening the muscles, making them isotonic. Though a common link between both types of exercise plans is that they are potential muscle strengtheners.
CONCLUSION
There is a close link between fitness and the medical world. They coincide on some levels, helping people to gain their particular needs. While the fitness fanatics are marvelled by the extraordinary muscular gains through isokinetic exercises, some patient is regaining their normal muscle strength lost during an unfortunate incident with the help of isokinetic equipment. The dynamometer is the brain of the isokinetic workout plan.
The operation of the machine may be a little challenging but once mastered, the strengths and scopes of improvement of one’s body will be at the fingertips. Professionals are required to handle the machine and give you the proper feedback. Well, technology comes with shortcomings. Being well versed with the technicalities of the isokinetic exercise equipment is essential.
Experts recommend going for light strength-based workouts before jumping to the isokinetic routine. Proper warm-up and hydration of the body are required for optimal functioning. You should get an appointment with your trainer to discuss your next positive body goal. We know you are psyched up to get your new workout routine with isokinetic.